Pakistan Institute of Development Economics
- Home
Our Portals
MenuMenuMenuMenuMenuMenuMenu - ResearchMenuMenuMenuMenuMenuMenuMenu
- Discourse
- The PDR
- Our Researchers
- Academics
- Degree Verification
- Thesis Portal
- Our Portals
High Rise, Town-Planning & Current Urban Paradigm of Pakistan
Dr. Ghulam Sarwar Sandhu is a former Director General CDA and is a town planner by profession. His views are that Town planning is the driver of sustainable development planning.
The situation of the Urban population: Looking back on history, globally, the rural component had a higher number than the urban population till 2008. Post-2009, the urban population started growing. The migrated population from rural to urban areas concentrated in a few specific urban centers resulting in unequal distribution and uncontrolled Urban centers. In last 50 years there have been a rapid increase in urbanization around the globe. Some UN calculations show that 55% of the world population will rise to 68% by the year 2050, 2.5 billion people will be added to urban areas by 2050; about 90% of this distribution would take place in Africa and South Asia.
The concentration of the population in fewer urban centers is causing the problems mentioned in Figure 1. All these problems result in a non-conducive environment for sustainable development of the cities, i.e., decreased economic activities. If we take an example of urban services present in metropolitan cities of Pakistan, they are inadequate in number. The concentrated population of Urban areas puts pressure on urban services, as shown in figure 2.
Figure 2 Urban Services in Metropolitan Cities of Pakistan
Development Plan/Master Plan is “ a plan for the future layout of a city and is a blueprint of the various proposals intended to improve the existing conditions and to regulate the future of growth of a town in a coordinated manner.” The functions of a master plan are to achieve the welfare of inhabitants, restrict haphazard and unplanned growth, integrate the urban infrastructure network, and incorporate development trends and needs. It is comfort, convenience, and well-being. The SGDs are both indirectly and directly linked with coordinated planning. But to reach SGDs, the unregulated and uncoordinated haphazard development hampers the Sustainable Development Strategies of Sustainable Cities and Communities (SGD) implementation. The elements of Sustainability are that they are socially acceptable, Environmentally Responsive, and Economically Viable.
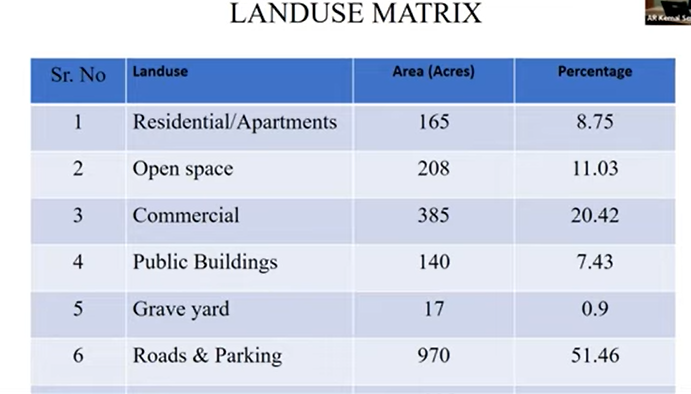
Islamabad Masterplan was developed in 1960, and all sorts of economic activities were incorporated while designing the city, whether the activities were related to agriculture, business, research institutes, or industrial development. Specified areas to generate economic activities that meet the requirement of daily needs of the people and availability of resources within walking distance. The population size of a city does not contribute to the development of a master plan due to the rapid growth of urban population, but a master plan has its own legal life, as of which the current master plans legal life was till 1985, and after that, it had to be revised, and vertical development was to be included in different sectors of Islamabad.
The existing master plan is car-centric. Traveling between different sectors requires a car as a means of transportation and limited resources for pedestrian use. By looking into a master plan of a sector, it was discussed that it had schools, shopping centers, parks, and colleges. These services are present in all sub-sector levels within walking distance, and at a wider angle, a community core is present for large-scale economic activity present in walking distance, also commonly known as Markaz.