Pakistan Institute of Development Economics
- Home
Our Portals
MenuMenuMenuMenuMenuMenuMenu - ResearchMenuMenuMenuMenuMenuMenuMenu
- Discourse
- The PDR
- Our Researchers
- Academics
- Degree Verification
- Thesis Portal
- Our Portals
Corporate Accountability: A Conduit to Combat Climate Change
Corporate Accountability: A Conduit to Combat Climate Change
(Anjeela Khurram, PIDE)
Scientists attribute the main cause of prevalent climate conditions to human activities. Since 1950, the global warming trend is ascribed to anthropogenic expansion of greenhouse effect. Anthropogenic or human induced warming signifies the component of that warming, which is attributable to human activities. The onset of industrial era has adversely changed the natural pattern of climate. For example, the carbon dioxide level over the last 400,000 years has remained below 300 ppm and this has skyrocketed from 1950’s to present (Figure 1).
Figure 1 shows that contrast that before the industrial revolution, the climate changes were natural, but onward the current climate change is largely anthropogenic.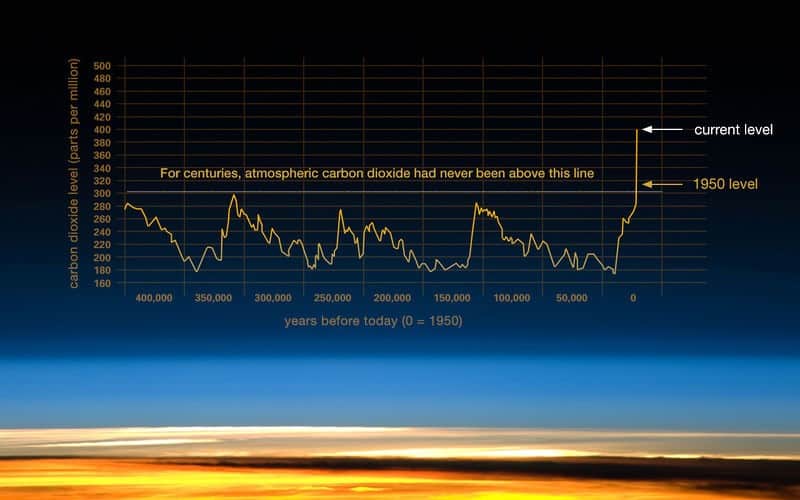 Figure 1:
Figure 1:
Change in CO2 levels in pre and post-industrial times
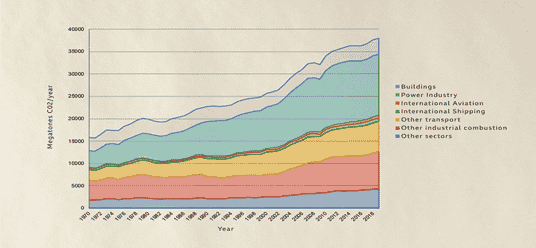
In the anthropogenic era, the CO2 level has increased from 280 parts per million to about 417 parts per million, since 1950. As a result, the global temperature has increased up to 1.5 °C above pre-industrial level, which has adverse impacts on the environment. This situation needs immediate attention. To tackle global warming, the need is to know which sectors are contributing the most to it. Among many, the corporate operations are the main root cause of pollution and global warming. The routine operations of corporate sectors like transportation, manufacturing, construction, agricultural and some others are emitting pollutants into the environment (Figure 2). The burning of fossil fuels, industrial activities and transportation are the main causes of greenhouse gases (GHG) concentrations, pollutant wastes and heat production and the subsequent global warming. The global warming, thus, results into glacier retreat, extreme weather, rise in sea-level, increase in land and ocean temperatures, lengthen frost-free season, changes in precipitation patterns, more droughts, heat waves, strong and intense hurricanes etc. The climate change has severe impacts on land and marine ecosystems. To curb this evil, there is a dire need on the part of companies to address the impacts of corporate activities on climate change by taking various proactive measures. Realizing this need, companies have thus made corporate accountability a governance mechanism to show their performance in non-financial areas such as social responsibility and sustainability.
Therefore, companies are positioning themselves as the steward of nature, in terms of climate change. The legal and societal expectations that companies should play their role to eliminate or reduce factors causing climate change are making companies more accountable. Likewise, there has been a significant increase in litigations to introduce a binding requirement to hold companies responsible for the impacts of climate change. Such litigations provide real opportunities for corporate accountability. These litigations introduce regulatory oversights for businesses and a liability mechanism for companies. Therefore, the legislations by coupling due diligence obligations with various other modes of accountability have the potential to ensure corporate accountability for climate change. Thus, the regulatory systems can be instrumentalized for climate purposes. The growing desire for corporate climate accountability is manifested in the fact that the litigations have included environmental, social and governance (ESG) requirements and accountability mechanisms to entail legal implications for companies. The ESG criteria are benchmarks set by related authorities for company’s operations to attract socially conscious investors. This is well evident in the current legislative developments targeting to ensure that companies should consider the impacts of their externalities on environment.
In order to comply with the environmental laws, the corporates accountability can ensure that companies are taking certain measures to play their part to reduce their externalities. The corporate governance mechanism should set some benchmarks to enhance the major stakeholders’ accountability. Shareholders of companies, being vital investors can ensure compliance with climate regulations. Similarly, the companies should stop practicing the tactics of Greenwashing to give the impression of eco-friendly vision. The regulatory authorities can track compliance or violations of laws by tracking the impacts of the corporate operations on environment and can execute prosecution in case of violations. The companies can play their part to tackle the climate crisis by switching to efficient renewable and clean energy sources, by conserving water resources through efficient water management, by increasing recycling to prevent waste accumulation and by monitoring the GHG emissions on daily basis. Likewise, the companies can develop mitigation and adaptation measures to manage impacts of their operations on climate change. Besides, the companies can adopt power management options, and can help developing markets for sustainable technologies and eco-friendly products and services. The corporate accountability is a mechanism set in companies to ensure that companies should comply with all applicable federal and state regulations concerning environment, energy and human rights to eliminate or reduce the causes of climate change.